Distinguishing between Market Order and Limit Order: Definition and Outstanding Features
A Comprehensive Guide to Market Orders and Limit Orders
In the realm of stock trading and investing, understanding the types of orders you can place is crucial. Two of the most common orders that traders use are Market Orders and Limit Orders. These orders serve as instructions to brokers on how to execute a trade on behalf of the trader. In this guide, we’ll delve deep into the definitions, differences, and nuances of these two order types.
Definitions
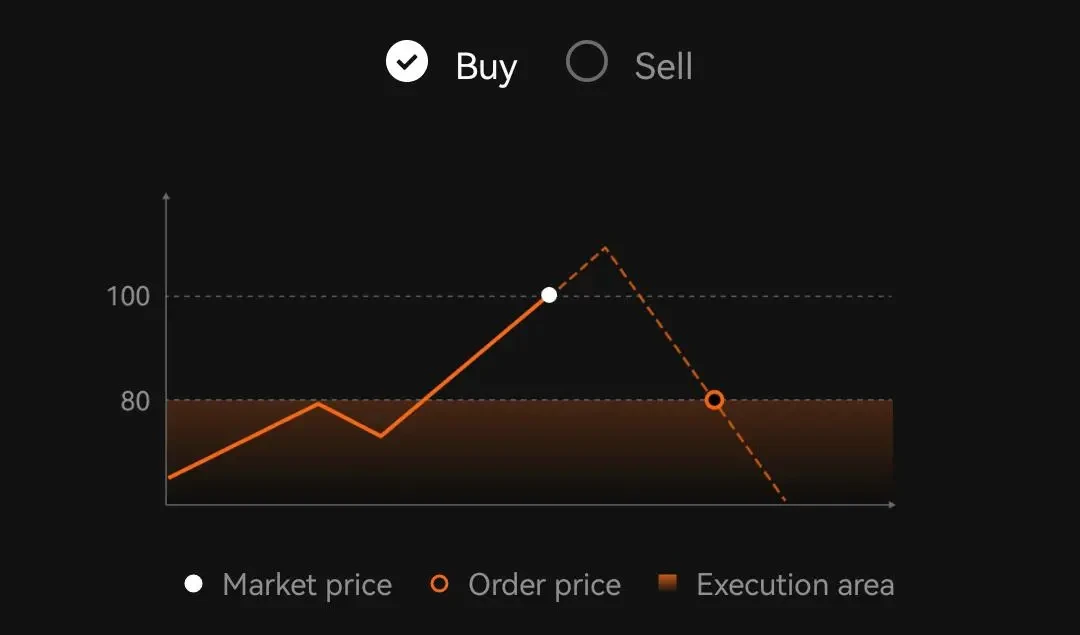
Market Order: A market order is a request made by an investor to purchase or sell a security at the best available price in the current market. It is designed for immediate execution and, given the liquidity in the market, is almost always filled. When an investor places a market order, they prioritize speed over price, ensuring that the order gets executed, but not necessarily at the best possible price.
Limit Order: A limit order, on the other hand, is an order to buy or sell a security at a specific price or better. This means that the trade will only be executed if the market price of the security reaches the trader’s desired price. Unlike market orders, limit orders are not guaranteed to be executed, but they do ensure that the trader does not pay more (or receive less) than the price they’ve set.
Differences between Market Orders and Limit Orders
Execution Priority:
Market Order: Prioritizes execution over price. It gets executed immediately at the current market price.
Limit Order: Prioritizes price over execution. It only gets executed when the stock reaches the specified price or better.
Price Assurance:
Market Order: Does not guarantee a specific price. The final executed price may differ from the current market price, especially in volatile markets.
Limit Order: Guarantees that the order will not be executed at a worse price than specified. However, it doesn’t guarantee the execution of the order itself.
Duration:
Market Order: Typically gets filled immediately, given there’s enough liquidity in the market.
Limit Order: Can remain open until the price condition is met or until the trader cancels the order. Some limit orders may expire if not executed within a specified timeframe.
Suitability:
Market Order: Suitable for traders who want to buy or sell quickly, without waiting for a specific price.
Limit Order: Ideal for traders who have a specific price in mind and are willing to wait for the market to reach that price.
Both market orders and limit orders have their own set of advantages and drawbacks. While market orders offer immediacy, they lack the price assurance that limit orders provide. Conversely, limit orders give traders more control over the price at which they’re willing to trade but come with the risk of the order not being executed at all.
The Benefits of Using Limit Orders: Ensuring Price and Gaining Better Control Over Trade Execution
In the vast landscape of stock trading, the tools and strategies you employ can significantly impact your investment outcomes. One such tool that has garnered attention and widespread usage among traders is the Limit Order. While we’ve previously delved into what a limit order is, in this guide, we’ll focus on its benefits, particularly in ensuring the price of a trade and providing better control over trade execution.
Introduction to Limit Orders: A Quick Recap
Before diving into the benefits, let’s quickly recap what a limit order is. A limit order is an instruction given to a broker to buy or sell a stock at a specific price or better. Unlike market orders, which execute immediately regardless of the stock’s current price, limit orders only execute when the stock reaches the trader’s desired price. This distinction brings us to the first significant benefit of limit orders.
Ensuring the Purchase or Sale Price
Price Protection: One of the primary advantages of using a limit order is the assurance it provides on price. When you set a limit order, you’re essentially setting a threshold, stating, “I don’t want to pay more than this price to buy” or “I don’t want to receive less than this price to sell.” This level of specificity ensures that you’re not caught off guard by sudden market fluctuations.
Avoiding Emotional Decisions: By setting a predetermined price, traders can avoid making impulsive decisions based on market volatility or emotional reactions. This can be particularly beneficial during times of rapid price changes, where emotions might otherwise lead to rash decisions.
Beneficial in Illiquid Markets: In markets where a stock isn’t traded as frequently, the difference between the bid (buy) and ask (sell) price can be substantial. A limit order can ensure that traders don’t end up buying a stock at a significantly higher price or selling at a much lower price than intended.
Gaining Better Control Over Trade Execution
Strategic Planning: Limit orders allow traders to plan their trades strategically. By setting a specific price, traders can aim to buy low and sell high, maximizing potential profits. This proactive approach contrasts with reactive strategies, where traders respond to the market’s current conditions.
Time Flexibility: Limit orders can be set for extended periods, allowing traders to wait for the market to reach their desired price without constantly monitoring it. This is especially beneficial for those who can’t keep a constant eye on the market.
Partial Fills and Multiple Transactions: Sometimes, there might not be enough volume to fulfill an entire order at the desired price. In such cases, a limit order can be partially filled, ensuring that at least a portion of the order is executed at the preferred price. Additionally, if a stock reaches the set price multiple times, a limit order can lead to multiple transactions, ensuring the trader gets the best price each time.
Avoiding Market Manipulation: In some cases, large market orders can influence stock prices, either driving them up or down. By using limit orders, traders can avoid unintentionally impacting the market with their trades.
Limit orders offer traders a level of precision and control that’s hard to achieve with other types of orders. By ensuring the purchase or sale price and providing better control over trade execution, limit orders can be a valuable tool in a trader’s arsenal.
However, it’s essential to remember that while limit orders offer numerous benefits, they come with their own set of risks, primarily the risk of the order not being executed at all. As with all trading strategies and tools, it’s crucial to understand the mechanics and implications fully. Always consider your individual investment goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions before placing a trade. And as always, thorough research and consultation with financial professionals can provide additional insights and guidance.
The Legality of Limit Orders: Broker Instructions and Regulations on Price and Timing
In the intricate world of stock trading, understanding the legal framework surrounding various tools and strategies is paramount. Among these tools, the Limit Order stands out not only for its strategic advantages but also for its legal implications. This guide will delve into the legal aspects of limit orders, focusing on their role as instructions for brokers and the regulations governing their price and execution timing.
Introduction: The Essence of Limit Orders
Before diving into the legal intricacies, it’s essential to reiterate what a limit order is. A limit order is a directive given to a broker to buy or sell a security at a specific price or better. Unlike market orders, which prioritize immediate execution, limit orders are contingent on the market price reaching the trader’s specified price.
Limit Orders as Instructions for Brokers
Clear Directives: Limit orders serve as clear, unequivocal instructions to brokers. When a trader sets a limit order, they’re essentially telling their broker, “Do not execute this trade unless the stock reaches my specified price.” This clarity ensures that brokers have a definitive guideline to follow, reducing the potential for misunderstandings or errors.
Binding Commitment: Once a limit order is placed, it becomes a binding commitment, provided it meets all regulatory requirements. This means that once the conditions of the order are met (i.e., the stock reaches the specified price), the broker is legally obligated to execute the trade.
Broker’s Discretion: While limit orders are explicit in terms of price, they don’t typically dictate the exact timing or method of execution. This leaves brokers with some discretion on how best to execute the order while still adhering to the trader’s price directive.
Regulations on Price and Execution Timing
Price Regulations:
Best Execution Obligation: Brokers are legally required to provide the best execution reasonably available for their clients’ orders. This means that if a trader sets a limit order and the market price reaches or surpasses that limit, the broker must execute the trade at that price or better.
Protection from Manipulation: Regulatory bodies have established rules to prevent market manipulation. These rules ensure that traders cannot place limit orders with the sole intention of influencing stock prices without the genuine intent to trade.
Timing and Execution:
Good-Til-Canceled (GTC) vs. Day Orders: Traders can specify the duration for which a limit order remains active. A Good-Til-Canceled order remains in effect until the trader cancels it or it’s executed. In contrast, a Day Order expires at the end of the trading day if not executed.
Partial Fills: In some cases, there might not be enough volume to fulfill an entire order at the desired price. Regulations allow for limit orders to be partially filled, ensuring that traders can still benefit from their specified price even if the entire order isn’t executed.
Order Expiry: Some limit orders come with an expiration date, after which they become void if not executed. Regulatory bodies have guidelines on how these expirations are handled to ensure transparency and fairness.
The legal framework surrounding limit orders is designed to strike a balance between providing traders with flexibility and ensuring market integrity. By serving as clear instructions for brokers and being governed by regulations on price and timing, limit orders offer traders a tool that’s both strategic and legally robust.
However, as with all trading tools, it’s crucial for traders to understand the legal implications fully. This understanding ensures that they can navigate the market effectively while staying within the bounds of the law. Always consider consulting with legal or financial professionals to gain a deeper understanding of the regulations and to ensure compliance.
A Deep Dive into Stock Order Types: Understanding LO Orders at Opening and Limit Orders at Closing
The stock market is a complex ecosystem, and navigating it requires a deep understanding of the various tools and strategies at a trader’s disposal. Among these tools, the types of orders one can place play a pivotal role in shaping a trader’s experience and outcomes. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore two specific types of stock orders: LO (Limit Order) at the opening session and Limit Orders at the closing session.
Introduction to Stock Order Types
Before delving into the specifics, it’s essential to understand that stock orders are directives given by traders to brokers, indicating how they want to buy or sell securities. The type of order determines factors like the price, timing, and conditions under which a trade is executed.
LO (Limit Order) at the Opening Session
Definition: An LO order at the opening session is a limit order that is placed before the market opens and is executed as close to the opening price as possible. It’s a strategic move for traders who want to capitalize on the price dynamics that occur at the beginning of the trading day.
Key Features:
Price Limitation: Like all limit orders, an LO order at the opening session specifies the maximum price a buyer is willing to pay or the minimum price a seller is willing to accept.
Timing: These orders are executed right at the market’s opening, leveraging the initial price movements that often result from overnight news or events.
Benefits:
Strategic Entry: For traders who anticipate significant price movements at the start of the trading day, this order type offers a strategic entry point.
Price Assurance: The order ensures that traders don’t pay more (or receive less) than their specified price, even amidst the volatility of the market’s opening.
Limit Orders at the Closing Session
Definition: A limit order at the closing session is designed to be executed as close to the market’s closing price as possible. It’s a strategy often employed by traders who want to capitalize on the end-of-day price dynamics or ensure their trade is executed before the market closes.
Key Features:
Price Specification: Traders set a specific price, and the order will only be executed if the market price reaches or surpasses that limit by the end of the trading day.
End-of-Day Execution: These orders are geared towards the market’s closing, aiming to capture any last-minute price movements.
Benefits:
Strategic Exit or Entry: For traders looking to close out positions or enter the market based on end-of-day trends, this order type offers a strategic point of action.
Protection Against Overnight Risk: By ensuring a trade is executed before the market closes, traders can mitigate the risks associated with overnight events or news that might impact stock prices.
Both LO orders at the opening session and limit orders at the closing session offer traders unique strategic advantages, tailored to the specific dynamics of the market’s opening and closing. By understanding these order types and their implications, traders can make more informed decisions, aligning their strategies with their investment goals and risk tolerance.
However, as with all stock market tools and strategies, it’s crucial to approach these order types with a thorough understanding and a well-researched strategy. Always consider consulting with financial professionals or conducting in-depth research to ensure you’re making informed trading decisions.
Mastering the LO Limit Order: Advantages, Disadvantages, and Comparisons with Market Orders
In the intricate world of stock trading, the tools and strategies you employ can significantly shape your investment outcomes. Among the myriad of order types available to traders, the LO (Limit Order) stands out for its unique characteristics and strategic implications. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the LO limit order, exploring its advantages, disadvantages, and how it compares to the more commonly known market order.
Introduction to the LO Limit Order
The LO limit order, often simply referred to as a limit order, is a directive given to a broker to buy or sell a security at a specific price or better. Unlike market orders, which prioritize immediate execution, LO limit orders are contingent on the market price reaching the trader’s specified price.
Advantages of Using the LO Limit Order
Price Assurance: One of the primary benefits of the LO limit order is the price guarantee it offers. Traders can set a maximum purchase price or a minimum sale price, ensuring they don’t overpay or undersell based on market volatility.
Strategic Planning: LO limit orders allow traders to set their price targets in advance, enabling them to execute trades at desired price points, which can be particularly beneficial in volatile markets.
Cost Efficiency: By setting a specific price, traders can potentially achieve better pricing compared to immediate market orders, especially in fast-moving markets.
Protection from Market Volatility: In rapidly fluctuating markets, LO limit orders protect traders from buying at peaks or selling at troughs.
Disadvantages of Using the LO Limit Order
No Execution Guarantee: The most significant drawback of the LO limit order is that there’s no guarantee the order will be executed. If the market price doesn’t reach the specified limit, the trade won’t occur.
Missed Opportunities: If a stock’s price moves favorably but doesn’t hit the exact limit set, traders might miss out on a beneficial trading opportunity.
Partial Fills: In situations where there isn’t enough trading volume at the specified price, an LO limit order might only be partially filled.
LO Limit Order vs. Market Order: A Comparison
Execution Priority:
LO Limit Order: Prioritizes price over speed. The order will only execute when the stock reaches the specified price or better.
Market Order: Prioritizes speed over price. It aims for immediate execution at the current market price.
Price Assurance:
LO Limit Order: Guarantees that the trader will not pay more (or receive less) than a specified price.
Market Order: Does not offer any price guarantee. The final executed price can differ from the current market price, especially in volatile conditions.
Execution Guarantee:
LO Limit Order: There’s no guarantee that the order will be executed, as it’s contingent on the stock reaching the set price.
Market Order: Almost always guarantees execution, provided there’s enough liquidity in the market.
The LO limit order offers traders a strategic tool that provides price assurance and potential cost efficiencies. However, like all tools, it comes with its own set of challenges, primarily the risk of non-execution. When deciding between an LO limit order and a market order, traders must weigh the importance of price assurance against the need for immediate execution.
As always, a well-informed trader is a successful trader. It’s crucial to understand the nuances of each order type fully and to align your trading strategy with your investment goals and risk tolerance. Consider consulting with financial professionals or conducting thorough research to ensure you’re making the best decisions for your unique situation.
A Comprehensive Guide to Market Orders on VMEX: Usage and Key Considerations
In the evolving landscape of digital trading platforms, VMEX has emerged as a notable player, offering traders a plethora of tools and functionalities to optimize their trading experience. One of the fundamental tools available to traders on VMEX is the market order. In this detailed guide, we’ll explore how to use market orders on VMEX and the essential considerations to keep in mind when placing them.
Introduction to Market Orders on VMEX
VMEX, like many trading platforms, provides its users with the ability to place market orders. A market order is a request by a trader to buy or sell a security at the best available price in the current market. It’s designed for immediate execution, ensuring that traders can enter or exit positions swiftly.
Using Market Orders on the VMEX Platform
Accessing the Trading Interface: Begin by logging into your VMEX account and navigating to the trading interface. This is where you’ll see a real-time overview of market movements, charts, and order placement options.
Selecting the Desired Security: Use the search bar or the dropdown menu to select the security you wish to trade.
Choosing the Market Order Option: Once you’ve selected the security, locate the order type options. Click on ‘Market Order’ to select it.
Entering the Quantity: Specify the number of units (shares, contracts, etc.) you wish to buy or sell.
Confirming the Order: Before finalizing, you’ll see an estimated price based on the current market rate. Click ‘Confirm’ or ‘Place Order’ to execute the trade. Remember, due to the nature of market orders, the final executed price may vary slightly from the estimated price.
Key Considerations When Placing Market Orders on VMEX
Price Volatility: Given that market orders are executed at the best available price, there’s a risk of slippage, especially in volatile markets. Slippage occurs when the executed price is different from the expected price. Always monitor market conditions before placing a market order.
Immediate Execution: Market orders are designed for speed, not price assurance. If immediate execution is your priority, a market order is suitable. However, if you have a specific price in mind, consider other order types like limit orders.
Platform Fees: Always be aware of any trading fees or commissions associated with executing trades on VMEX. These fees can impact the overall profitability of your trades.
Partial Fills: In situations where there isn’t enough liquidity to fulfill your entire order, you might experience a partial fill. This means only a portion of your order is executed.
Stay Updated: VMEX, like all trading platforms, undergoes updates and changes. Always familiarize yourself with the latest platform features and functionalities to optimize your trading experience.
A Comprehensive Guide to Limit Orders on Yuanta: Step-by-Step Instructions and Key Considerations
In the dynamic world of online trading platforms, Yuanta stands out as a robust and user-friendly platform, offering traders a wide range of tools to enhance their trading experience. Among the various order types available on Yuanta, the limit order is a fundamental tool that traders often utilize. In this detailed guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of placing a limit order on Yuanta and highlight the essential points to consider when using this order type.
Introduction to Limit Orders on Yuanta
Yuanta, like many advanced trading platforms, provides its users with the option to place limit orders. A limit order is a directive given by a trader to buy or sell a security at a specific price or better. Unlike market orders, which aim for immediate execution, limit orders are executed only when the security’s market price matches the trader’s specified price.
Placing a Limit Order on the Yuanta Platform
Accessing the Trading Interface: Start by logging into your Yuanta account. Once logged in, navigate to the trading interface, where you’ll be presented with real-time market data, charts, and various trading options.
Selecting the Desired Security: Locate the search bar or use the provided dropdown menus to select the security you’re interested in trading.
Choosing the Limit Order Option: Upon selecting the security, you’ll be presented with different order type options. Click on ‘Limit Order’ to proceed.
Specifying the Price: Enter the price at which you wish to buy or sell the security. This is the price you’re willing to pay (for buying) or accept (for selling).
Entering the Quantity: Specify the number of units you wish to trade – this could be shares, contracts, or other units depending on the security.
Review and Confirm: Before finalizing the order, review all the details. Ensure that the price and quantity are correct. Once satisfied, click ‘Place Order’ or ‘Confirm’ to set the limit order.
Key Points to Consider When Using Limit Orders on Yuanta
No Execution Guarantee: One of the primary things to remember about limit orders is that execution is not guaranteed. If the market price doesn’t reach your specified price, the order won’t be executed.
Market Volatility: In highly volatile markets, even if the market price reaches your specified limit, rapid price fluctuations might result in non-execution. It’s essential to monitor such conditions closely.
Duration of the Order: Yuanta might offer options like ‘Day Order’ or ‘Good-Til-Canceled’ for limit orders. Ensure you select the appropriate duration based on your trading strategy.
Platform Fees: Always be aware of any associated trading fees or commissions on Yuanta. These can impact the overall profitability of your trades.
Continuous Monitoring: While limit orders provide a level of automation, it’s beneficial to monitor your orders regularly, especially in fast-moving markets, to ensure they align with your trading strategy.
Stay Updated: Yuanta, like all trading platforms, undergoes periodic updates and changes. Ensure you’re familiar with the latest features and functionalities to make the most of your trading experience.
Limit orders on Yuanta offer traders a strategic tool that provides a balance between price assurance and potential execution. By understanding how to place a limit order on Yuanta and being aware of the associated nuances, traders can make informed decisions that align with their investment objectives.
Continuous learning and staying updated with both the platform’s features and broader market trends are crucial for a successful trading journey on Yuanta. Always consider consulting with financial professionals or conducting thorough research to ensure you’re making the best decisions for your unique situation.
Harnessing the Power of Limit Orders on ACC Group: Definition, Usage, and Benefits
In the fast-paced world of online trading, the ACC Group has emerged as a trusted platform for traders worldwide. Among the myriad of tools and functionalities it offers, the limit order stands out as a fundamental instrument for strategic trading. This comprehensive guide will delve into the nature of limit orders on the ACC Group platform, exploring its definition, characteristics, usage, and inherent benefits.
Definition and Characteristics of Limit Orders on ACC Group
Definition: A limit order, as facilitated by ACC Group, is a directive given by a trader to buy or sell a security at a predetermined price or better. Unlike market orders, which seek immediate execution at the prevailing market price, limit orders are executed only when the security’s market price aligns with the trader’s specified price.
Key Characteristics:
Price Specificity: Limit orders allow traders to set a precise price for a security, ensuring that they neither pay more (when buying) nor receive less (when selling) than their desired price.
Conditional Execution: The execution of a limit order is contingent upon market conditions. If the market price never reaches the specified limit, the order remains unexecuted.
Duration Options: ACC Group may offer various durations for limit orders, such as ‘Day Order’ (expires at the end of the trading day) or ‘Good-Til-Canceled’ (remains active until executed or canceled by the trader).
Using Limit Orders on ACC Group and Their Benefits
Placing a Limit Order:
Access the Trading Interface: Log into your ACC Group account and navigate to the trading dashboard.
Choose the Desired Security: Use the platform’s search or filtering tools to select the security you wish to trade.
Select ‘Limit Order’: Upon selecting the security, you’ll be presented with order type options. Choose ‘Limit Order.’
Set Your Price: Enter the price at which you wish to execute the trade. This is your “limit.”
Specify Quantity: Indicate the number of units (e.g., shares) you intend to buy or sell.
Review and Confirm: Before submitting, review all details to ensure accuracy. Once satisfied, finalize the order.
Benefits of Using Limit Orders on ACC Group:
Price Control: Limit orders offer traders unparalleled control over the price at which they trade, ensuring they achieve their desired price points.
Cost Efficiency: By setting specific prices, traders can potentially secure better deals, especially in volatile markets where prices can fluctuate rapidly.
Strategic Trading: Limit orders allow traders to set their price targets in advance, enabling them to capitalize on market movements without constantly monitoring the market.
Risk Management: By setting a predetermined price, traders can effectively manage their risk, ensuring they don’t enter or exit positions at unfavorable prices.
Limit orders on ACC Group provide traders with a strategic tool that marries precision with potential. By understanding the nature and benefits of limit orders, traders can harness their power to optimize their trading outcomes on the ACC Group platform.
As with all trading tools, continuous education and staying abreast of both platform-specific features and broader market trends are crucial. Always consider consulting with financial experts or conducting in-depth research to ensure you’re making informed and strategic trading decisions
Mastering Market and Limit Orders on Binance: A Comprehensive Guide to Trading and Key Considerations
Binance, a name synonymous with cryptocurrency trading, has rapidly risen to prominence as one of the world’s leading crypto exchanges. With its user-friendly interface and a plethora of trading tools, Binance offers both novice and seasoned traders a platform to navigate the volatile world of cryptocurrencies. Among the essential tools available are the market and limit orders. In this detailed guide, we’ll explore how to place these orders on Binance and highlight crucial points every trader should consider.
Introduction to Market and Limit Orders on Binance
Market Orders: A market order on Binance is a request to buy or sell a cryptocurrency immediately at the best available current market price. It’s designed for swift execution, ensuring traders can quickly enter or exit positions.
Limit Orders: A limit order, in contrast, allows traders to specify a price at which they wish to buy or sell. The order will only be executed when the cryptocurrency’s market price matches the trader’s set price.
Placing Market and Limit Orders on Binance
Accessing the Trading Interface: Begin by logging into your Binance account. Navigate to the ‘Exchange’ or ‘Trade’ section to access the trading interface.
Selecting the Desired Cryptocurrency Pair: Use the search bar or dropdown menus to choose the cryptocurrency pair you’re interested in trading, such as BTC/ETH.
Placing a Market Order:
Choose the ‘Market’ tab from the order options.
Enter the amount of the cryptocurrency you wish to buy or sell.
Click ‘Buy’ or ‘Sell’ to execute the trade immediately at the current market price.
Placing a Limit Order:
Select the ‘Limit’ tab from the order options.
Specify the price at which you want to buy or sell.
Enter the quantity of the cryptocurrency.
Click ‘Buy’ or ‘Sell’ to place the order. It will be executed once the market price matches your specified price.
Key Considerations When Trading on Binance
Trading Fees: Binance charges a trading fee for every transaction. While these fees are relatively low, frequent traders should be aware of them as they can accumulate.
Market Volatility: The cryptocurrency market is known for its volatility. While market orders ensure quick execution, the final price might differ from the price seen when placing the order, especially during rapid price movements.
Order Book Visibility: Before placing a limit order, it’s beneficial to check the order book. This provides insights into the current buy and sell orders, helping traders make informed decisions.
Security Measures: Always ensure that you have two-factor authentication enabled on your Binance account. This adds an extra layer of security, safeguarding your assets.
Order Duration: Binance offers different durations for limit orders, such as ‘Good-Til-Canceled’ and ‘Immediate-Or-Cancel.’ Choose the one that aligns with your trading strategy.
Stay Updated: Binance frequently updates its platform and introduces new features. Staying updated ensures you make the most of what Binance has to offer.
Both market and limit orders offer Binance traders unique advantages tailored to different trading strategies. By understanding how to place these orders and being aware of the associated nuances, traders can navigate the Binance platform with confidence and precision.
Continuous learning and staying updated with both Binance’s features and broader crypto market trends are essential for a successful trading journey. Always consider consulting with financial professionals or conducting thorough research to ensure you’re making informed decisions in the dynamic world of cryptocurrency trading.
Comparing Trading Platforms and Choosing the Right Order Type: A Comprehensive Overview
In the vast realm of financial trading, the platform you choose and the type of order you place can significantly influence your trading outcomes. With a plethora of platforms available and a myriad of order types to navigate, making informed decisions becomes paramount. In this detailed guide, we’ll compare various trading platforms and delve into how to select the appropriate order type based on your trading objectives.
Comparing Trading Platforms
User Interface: While some platforms like Binance prioritize a feature-rich interface catering to seasoned traders, others might offer a more streamlined, user-friendly experience for beginners. The choice here depends on your familiarity with trading and your preference for simplicity or comprehensive tools.
Asset Variety: Platforms like VMEX might focus predominantly on specific asset classes, while giants like Binance offer a vast array of cryptocurrencies. Depending on your trading interests, the range of assets available can be a deciding factor.
Trading Fees: Every platform, from ACC Group to Yuanta, has its fee structure. Some might offer lower transaction fees but compensate with withdrawal charges. It’s essential to understand the complete fee breakdown to ensure cost-effective trading.
Security Measures: In the wake of numerous cyber-attacks on trading platforms, security has become a top priority for traders. Platforms with robust security measures, two-factor authentication, and cold storage solutions are often preferred.
Educational Resources: For novice traders, platforms that offer educational resources, tutorials, and customer support can be invaluable. This aids in understanding the trading landscape and making informed decisions.
Choosing the Right Order Type Based on Trading Objectives
Immediate Execution vs. Price Control: If your primary goal is to enter or exit a position immediately, market orders, which prioritize speed over price, are ideal. However, if you seek more control over the price at which you trade, limit orders, like those on Yuanta or VMEX, offer the precision you need.
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Strategies: For traders with a short-term focus, looking to capitalize on quick market movements, market orders or even stop-limit orders can be beneficial. Those with a long-term perspective, aiming for specific price points, might prefer limit or LO orders.
Risk Appetite: If you’re risk-averse, you might lean towards limit orders, which provide price assurance. On the other hand, if you’re willing to embrace some level of risk for immediate execution, market orders could be your go-to.
Trading Volume and Liquidity: In markets or assets with high liquidity, market orders are less likely to experience significant slippage. However, in less liquid markets, limit orders can offer protection against unfavorable price shifts.
The trading platform you choose and the order type you employ are reflections of your trading strategy, objectives, and risk tolerance. By understanding the nuances of various platforms and the implications of different order types, traders can navigate the financial markets with confidence and clarity.
Continuous education, staying updated with market trends, and periodically reassessing your trading objectives are crucial for success. Whether you’re trading on Binance, ACC Group, VMEX, or Yuanta, a well-informed trader is always better positioned to achieve their financial goals. Always consider consulting with financial experts or diving deep into platform-specific resources to ensure you’re making the best decisions for your unique trading journey.
